CALCUTIONS AREA
CLICK ON CALCULATOR
Infant Data
Results
MEDICAL INFORMATIONS
INDICATIONS
- Serious infections (bacteremia and meningitis): due to susceptible strains of streptococci (non enterococcal).
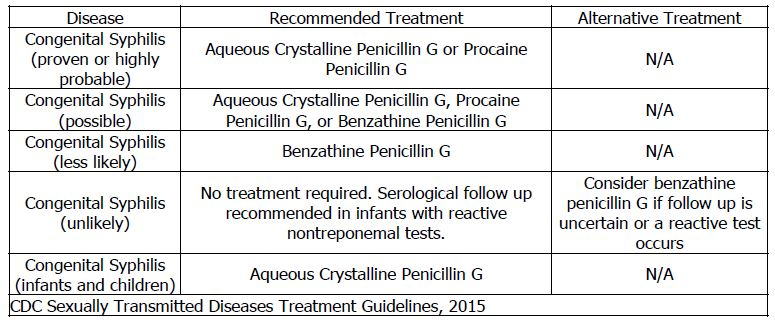
- Congenital syphilis: For congenital syphilis, aqueous crystalline penicillin G is recommended in neonates with proven or highly probable disease and :
- an abnormal physical examination consistent with congenital syphilis.
- a serum quantitative nontreponemal serologic titer that is fourfold higher than the mother’s titer;
- a positive darkfield test (or polymerase chain reaction) of body fluid(s) or lesions
- Also recommended in neonates who have a normal physical examination and a serum quantitative nontreponemal titer the same or less than fourfold the maternal titer and the:
- mother was not treated, inadequately treated, or has no documentation of having received treatment.
- mother was treated with erythromycin or another non-penicillin G regimen.
- mother received treatment less than 4 weeks before delivery.
- Group B Streptococcal (GBS) Disease(Definitive):The preferred antibiotic for early-onset and late-onset, culture confirmed-GBS disease is penicillin G and the alternative is ampicillin.
- Infective endocarditis: The following recommendations are based on a consensus of experts.The full pediatric guidelines can be found here:

- Anthrax:

ADVERSE EFFECTS
Cardiac arrest has been reported in patients who received high doses infused rapidly. Significant CNS toxicity has been reported in adults with renal failure who developed CS concentrations greater than 10 mcg/mL. Bone marrow depression, granulocytopenia, and hepatitis are rare. Hypersensitivity has not been seen in neonates.
ADMINISTRATION
Intravenous: Administer by IV intermittent infusion over 15 to 60 minutes at a concentration of 100,000 to 500,000 units/mL. Penicillin sodium contains 1.68 mEq sodium/million units and penicillin potassium contains 1.68 mEq potassium/million units and 0.3 mEq sodium/million units.
MONITORING
Follow serum sodium and potassium when using high doses and in patients with renal failure. Observe IV site for signs of extravasation.
